white and blue magnetic card
Photo by Avery Evans on Unsplash
Most companies attempting to drive customer loyalty fail miserably—and few so-called customer-centric companies generate sustainable customer loyalty that drives measurable business results. Why? Because they get three key principles completely wrong, right from the start:
- Loyalty is about the company acting loyally to its customers, not vice versa.
- It is about a loyalty approach, not a loyalty program.
- Loyalty is about the store, not only about the CRM.
1.Loyal to Customers
We start to act loyally to customers when we understand them to a level of detail that ensures that we remain responsive to changes in their behavior, relevant to ever-changing customer needs and rewarding in the way we treat customers.
Acting loyally is about adopting a loyalty mind set of managing customer segments as strategic business units (aligning with how we think about a category management strategy as managing categories as strategic business units). This context demands change that is both incremental and transformational—evolution, but with a bit of manageable revolution.
What customer loyalty is, and is not:
- Acting loyally (responsive, relevant, rewarding) to our customers; not about customers being loyal to us
- An overall approach throughout our business; not a proposition or program
- Earning customer loyalty; not thinking that customers should become loyal
- Collaborative partnerships to win customers together; not tolerant of internal conflict between areas of the business or with suppliers
- Transparent; not opaque
- Driving sales and cash margin; not customers being responsible for percent margin
2.Loyalty Approach vs. Loyalty Program
We demonstrate loyalty to our customers by taking a loyalty approach wherein we commit to rewarding and delighting our customers with products and experiences that meet their wants and needs.
- We call this putting customers first—when we decide on priorities and actions based on insights from our customer data.
- By doing so, a retailer becomes an even more prominent choice in the customer's consideration set. This is not a tactic; it is a long-term strategy that makes the customer the focal point of our business decisions and objectives.
The loyalty program is an important element within a loyalty approach, as the key source of the data that enables customer intelligence, and as the channel that enables us to talk to our customers personally. I call the loyalty program the "little l" in loyalty, with the loyalty approach as the "big L."
But a loyalty program is not required to act in a loyal way to customers. Here's how to think of "big L" loyalty:
A loyalty approach, simply put, embeds customer insight throughout the retail organization to enable better, faster decisions and thereby increase sales and profit sustainably. Best-in-class practitioners have seen an incremental sales uplift in the early stages of a loyalty approach of between 1% and 2% and later stages between 3% and 4%, quarter over quarter and year over year.
3.Loyalty Is About the Store, Not Just the CRM
As I used to say to my retail colleagues, "If the store is lousy but we deliver brilliant targeted CRM, the store will still be lousy."
Even if the personalized CRM is perfect, customers need to perceive that tangible changes have been made in the store itself before they will respond by giving more of their custom. We must put customer insights into action within the "hardwiring" of retail practices—pricing, promotion, assortment, adjacencies, new products, the checkout experience and so on.
In a previous article, I shared several examples of being loyal to customers in store by simply making the shopping experience easier—setting the yogurt section by customer need rather than by brand blocks, for example, and by setting product adjacencies according to how customers shop, rather than by how items are sourced in the supply chain.
3 Ways to Activate a True Loyalty Approach
- Make better business decision by putting the customer first. Everything is better when you start with the customer. Start with the data you hold on customers—understanding how they shop and behave, what is important to them and how they engage with your business. This insight will identify a number of opportunities for better decisions using the data.
- Improve the customer experience by using data-driven insights to improve your retail offering, such as assortment, pricing and promotions. Use insights to connect you to your customer through the store. Think of the mantra "data to insights to actions"—this is how improved like-for-like sales growth and customer loyalty is delivered.
- Transform the organization using customer-driven insight to help you better understand, anticipate, measure and continually respond to your customers. This is realized through empowering, aligning and equipping your people with relevant insights, values, goals, strategies and actions.
David Ciancio is Global Customer Strategist for Dunnhumby, a pioneer in customer data science, serving the world's most customer-centric brands in a number of industries, including retail. David has 48 years' experience in retail, 25 of which were in store management. He can be reached at David.Ciancio@dunnhumby.com
Keep Reading...Show less
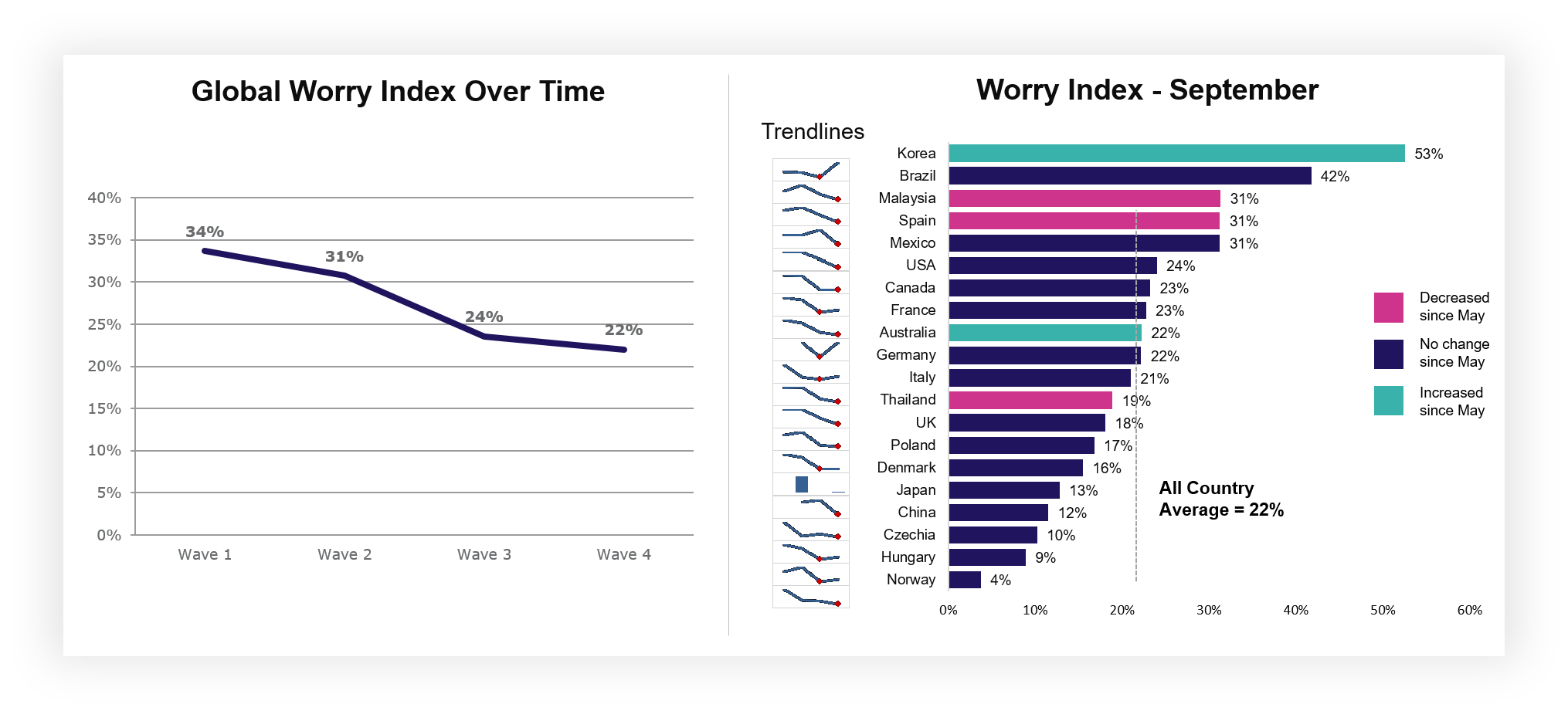
The dunnhumby Consumer Pulse Survey is a multi-phased, worldwide study of the impact of COVID-19 on customer attitudes and behavior. We surveyed more than 27,000 respondents online in 22 countries, with interviews conducted for Wave one from March 29 – April 1, for Wave two from April 11 – 14, and for Wave three from May 27 – 31. Due to the rapidly unfolding crisis in North America, dunnhumby conducted Wave four from July 9 – 12 in the U.S., Canada and Mexico only. Here are highlights from the study:
Keep Reading...Show less
In a series of posts published earlier this year, we covered the results of the dunnhumby Customer Pulse – a global study designed to explore changing consumer mindsets during the COVID-19 pandemic. Over three waves, conducted between March and the end of May, we polled thousands of people from more than 20 countries on subjects including supermarkets' responses to the outbreak, the economic outlook, and how their shopping behaviour had changed due to COVID.
At the beginning of September – three months on from the previous wave and with supply chains stable and the changing nature of lockdowns – we wanted to revisit the Customer Pulse to see what, if anything, had changed. Below are some of the standout findings from this fourth tranche of research.
Worries fade, but some still feel unsafe while shopping
One of the key things tracked by the Customer Pulse is something that we refer to as the "Worry Index" – a representation of how concerned consumers around the world are about COVID-19. Globally, the Index has now fallen to its lowest point, down from 34% in March to just 22% in September. Australia and Korea are the only countries to show a rise since the previous study, with the latter of those demonstrating the sole meaningful increase.
While worries may be dwindling generally, this can change rapidly based on local circumstances, and in-person shopping is still a point of concern for many: one third (33%) of those surveyed said they still don't feel safe from infection while shopping. Although this figure has fallen considerably since waves one (42%) and two (43%) of the Customer Pulse, this does mean it's of critical importance to retailers to keep communicating the efforts and importance of supporting colleagues and customers by focussing on positive drivers of a safe shopping experience and activities supporting vulnerable customers.
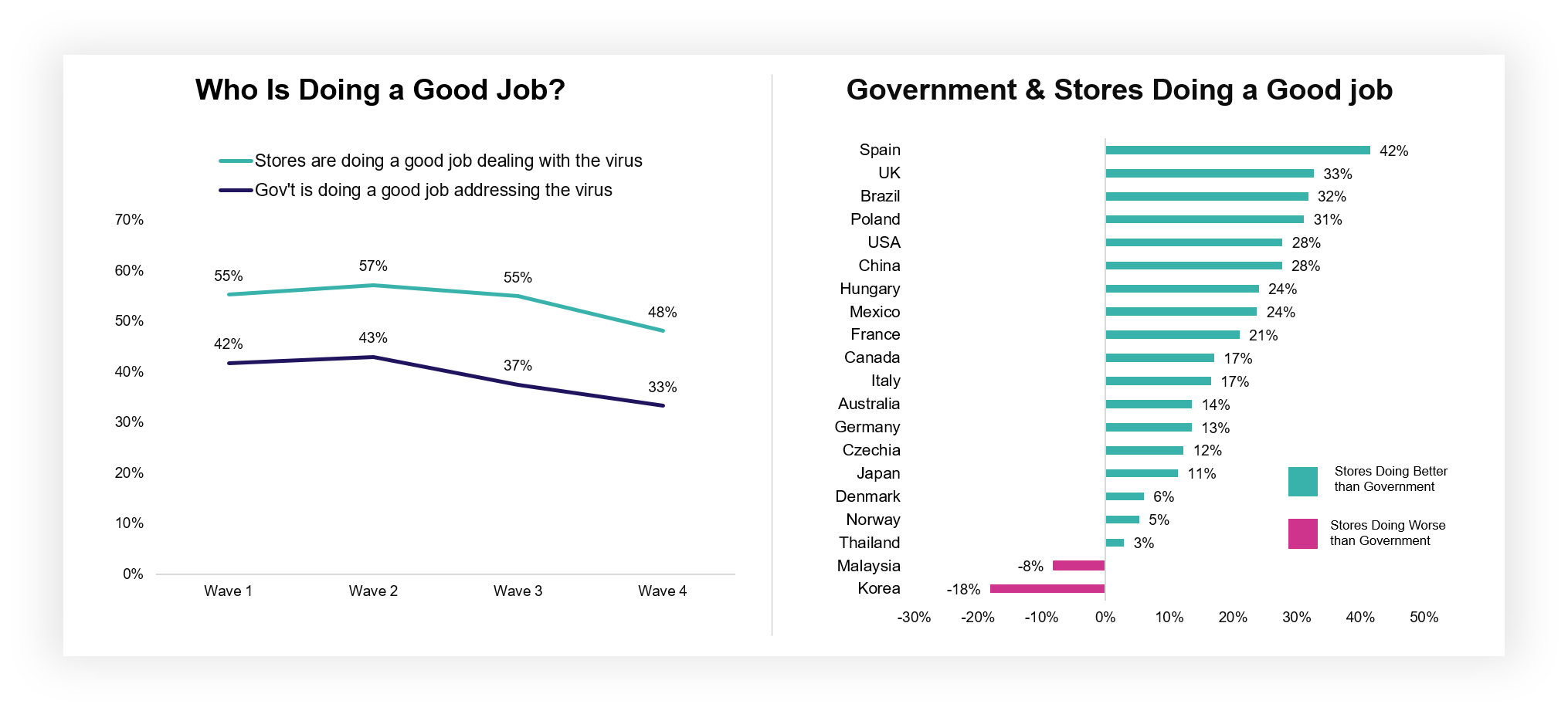
Those persistent worries should not detract from the phenomenal work the Grocery Retail industry has done to reassure Customers over the past six months. Stores (48%) continue to outpace the government (33%) in terms of who shoppers believe are doing a good job of dealing with the virus, a trend that has remained consistent across the duration of our study. Retailers in Canada, Australia and the UK are seen to be doing particularly well.
Early changes to shopping habits remain in place
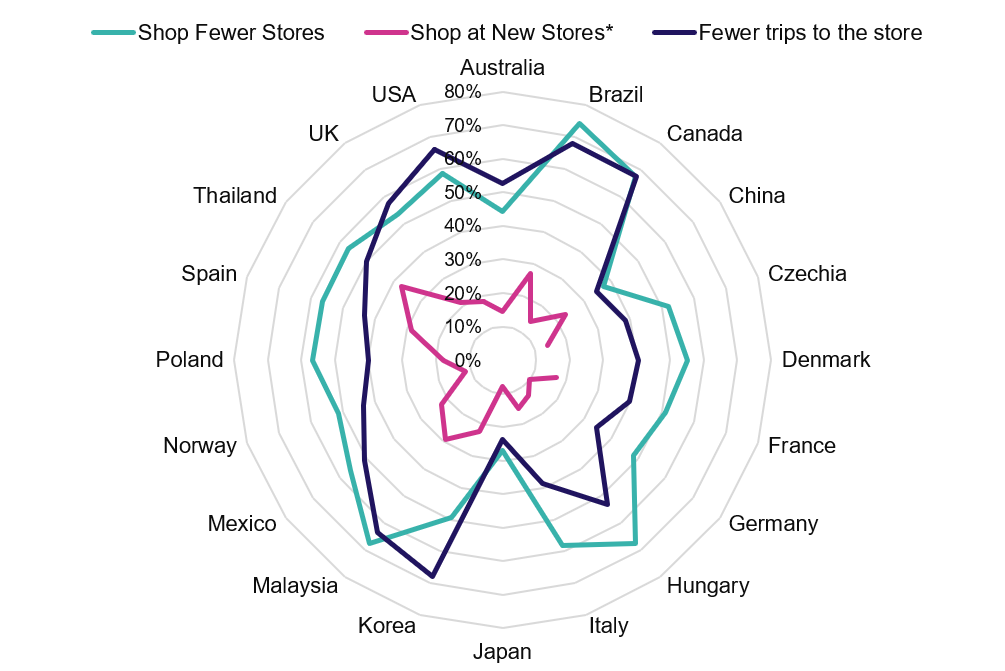
The early months of the pandemic saw major changes to Customer shopping behaviours. Trips decreased, as did the number of stores being visited, while basket sizes and ecommerce usage both skyrocketed.
Six months on from our initial survey, those behaviours remain largely unaffected. While the number of trips that Customers make has slightly risen, it has not done so with any degree of significance. Broadly, shoppers have continued to stay local, and visit stores only when they need to. Only a minority are shopping new stores.
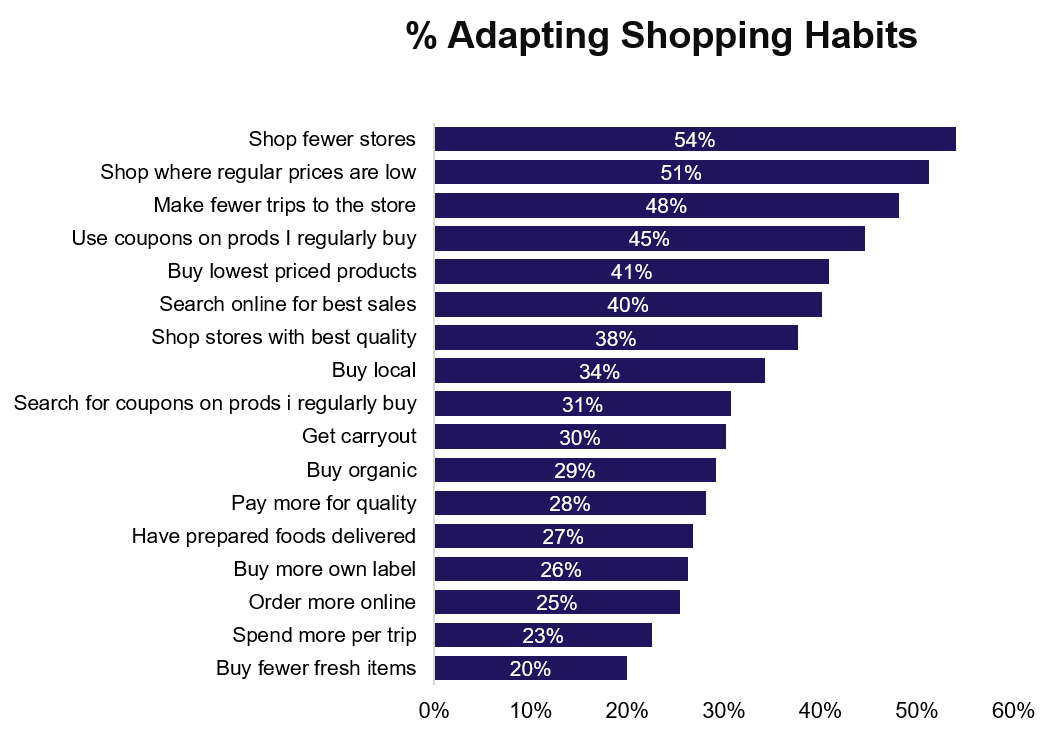
Consequently, many shoppers continue to spend more when they do shop; around a quarter (23%) say they are still spending more each trip. Basket sizes can fluctuate though and some markets saw spikes particularly sharply towards the end of September*, likely a consequence of infection rates beginning to rise once again and many shoppers wishing to stock up in the event that tighter restrictions could follow.
One the most profound changes in behaviour during the outbreak – the upsurge in online grocery – continues apace. Ecommerce now accounts for 28% of weekly shops, the same as it did in May, and relatively stable since the start of the pandemic when it stood at 30%. Many respondents plan to continue to adopt online alongside store shopping with 59% saying they plan to continue using online channel. The tipping point for online is well and truly here.
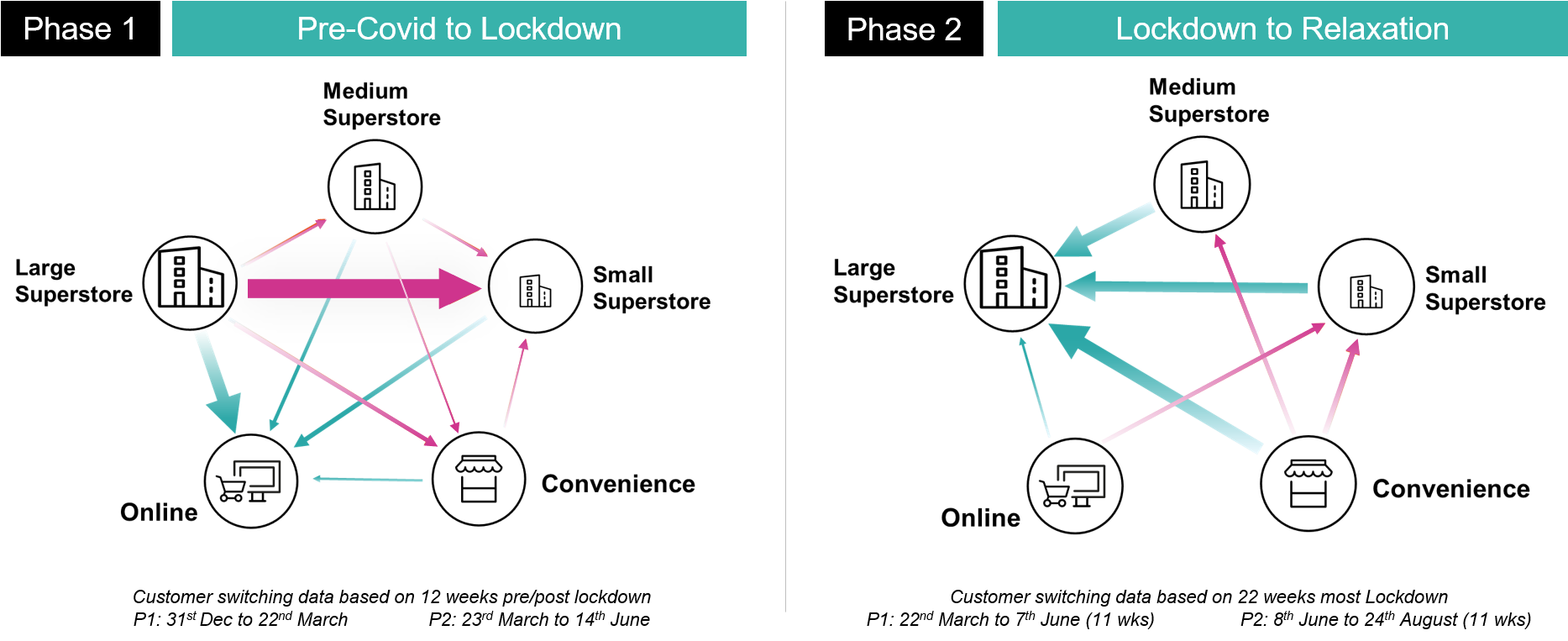
Although many of the pandemic-based trends have remained consistent during the past half year, some shifting dynamics are worth bearing in mind. In the UK specifically, while the initial outbreak saw large superstores lose much of their trade to both smaller shops and digital channels, much of that custom is now being pulled back in from small and medium stores, as well as convenience locations.
Financial worries have remained constant, and frugal behaviours are rising as a result
In regard to both their personal finances and the economic outlook for their country as a whole, many shoppers are now a little more optimistic than they were when the Customer Pulse began. That said, concern is still rife; around half (47%) of consumers have worries about their own financial situation, and more than two-thirds (67%) say the same about their national economy.
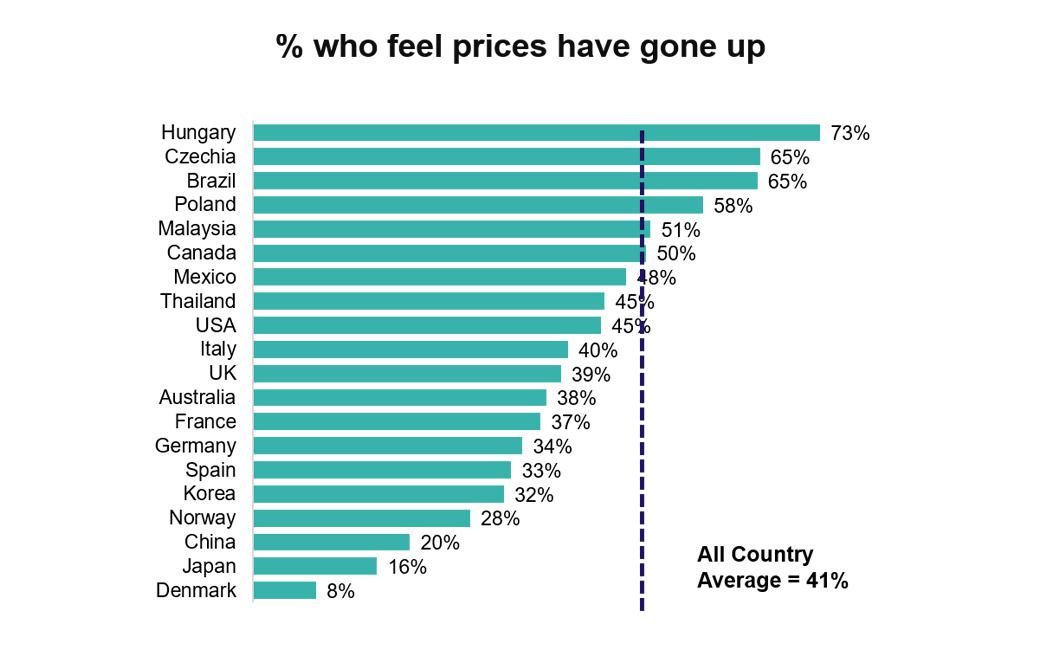
Accurately or not, this prolonged concern has translated into widespread belief that grocery shopping is becoming more expensive. Some 41% of global respondents believe that prices have risen, with many countries showing a significant increase since May. France is the only country in which this figure has declined.
The upshot of this persistent financial worry is that many Customers are now beginning to act more frugally. More than half (51%) are looking to lower-priced stores, with similar numbers increasing coupon usage (45%), opting for the lowest-priced goods (41%), and looking online for the best available sales. As we reported in June, a new age of value perception is here.
Eight important shifts will define the future for Grocery Retail
As Customer behaviours continue to flex around the impact of COVID-19, we believe that Retailers need to continue to focus on eight key shifts and business enablers as they continue to respond and future proof their business for the future. Consumer behaviours
- Value: as discussed above, demonstrating value to Customers will become increasingly important over the coming months with continued pressure on household budgets.
- Local: with shoppers preferring to stay local, range and assortment will need to be tailored as a result across formats.
- Food at home: despite recent increases in the number of people dining out, many shoppers continue to favour recreating meal experiences at home, both in cooking from scratch and food to go solutions from grocers.
- Personal wellbeing: a growing trend towards health, wellness, and better eating habits will need to be catered for.
Retailer adaptation
- Online: while the sharp rise in ecommerce adoption has now begun to plateau, utilisation remains significantly higher than it was pre-pandemic.
- Digital acceleration: with more Customers heading online, a greater opportunity to engage and inspire using digital channels comes into play.
- New revenue streams: with margins growing tighter as the cost of managing the Pandemic and online fulfilment rises, Retailers will need to find new sources of revenue to offset this expenditure. New retail services, and monetising data and media are key opportunity areas.
- Efficiency and SKU consolidation: related to the above, the need for Retailers to optimise and solidify their operations will become greater too with heightened focus on optimising and simplifying assortment.
For more information about COVID-19's impact on Grocery Retail, please visit our dedicated resource hub.
* Data from this edition of the Consumer Pulse has been supplemented with recent insights from HuYu, dunnhumby's receipt scanning and rewards platform.
Keep Reading...Show less
assorted fruits at the market
In the decade since Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein's Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth and Happiness was published, nudge theory has enjoyed unprecedented success.
Predicated on the idea that individuals respond better to indirect suggestion than outright commands, nudge theory is commonly used as a way of subtly influencing our behaviour towards positive choices. The idea has gained such traction, in fact, that many governments around the world have created "nudge units" in a bid to tackle thorny issues like obesity and the climate emergency.
Just as governments are exploring how nudge theory can be used to tackle real-world challenges, retailers have a similar opportunity with regard to their customers' dietary choices. With even a few small changes, retailers can help to nudge shoppers in the direction of healthier food decisions.
What follows are some of my favourite nudges that grocery retailers could easily implement to aid customer health.
Tackle the temptation of treats
In 2018[1], scientists published their findings from a seminal experiment in which some of the UK's leading retailers removed snacks and confectionery from the checkout. Purchases of sweets, chocolate, and crisps subsequently fell by 76% when compared to supermarkets that kept those items in place. In other words, just changing the location of products can nudge shoppers into healthier decision making.
Give healthier goods more space in-store
In 2012[2], scientists investigated whether the sale of healthy snacks next to the checkout in a hospital canteen could be influenced by the amount of shelf space they were allocated. Healthy products were given a quarter of the shelf space in the first test, and three-quarters in the second, with sales rising from just 14% to 44% as a result. Visible availability of healthier options clearly plays a big role in pushing us towards them.
Create dedicated “fruit and vegetable” partitions in trolleys
One particularly innovative nudge was discovered by a group of US scientists in 2017[3], who found that introducing an area in a trolley specifically for fruit and vegetables led to higher sales of those items. As with the previous example, the amount of space dedicated also had a role to play. In one study, increasing the size of the partition from 35% to 50% of the trolley increased customer spend on fruit and veg from $14.97 to $17.54.
Normalising fruit and veg purchases
Change4Life is a campaign run by the UK's Department of Health, aimed at nurturing healthier lifestyles. A 2015 study[4] commissioned as part of the campaign suggests that "normalising" the purchase of fruit and veg goes a long way towards influencing shoppers. When trolleys used statistics showing how many other shoppers purchased fruit and veg, spend in those categories rose by 12.4%. Social norm communications like this are a classic form of nudge that exploits our deep-seated concept of conformity (in this case in a very positive way!).
Use cartoon characters to encourage healthy eating amongst children
Obesity isn't just a problem for adults. To help tackle childhood obesity, the Food Dudes[5] programme put cartoon role models at the centre of its in-school campaigns. One London-based study found that fruit consumption amongst the poorest eaters increased from 4% to 68%, while an unexposed control group showed no change. Whilst this may not show increased consumption in a retail context, the concept of using accessible and entertaining imagery and characters to promote healthy eating out of store should be equally applicable in-store.
The new nudge on the block
Some of these techniques came together last year when the Royal Society for Public Health showcased Nudge, a pop-up at The People's Supermarket in London[6]. While the store was only open for two days, the purchase of sugary drinks was halved according to customer feedback. There are plans to make Nudge a permanent feature of the store, and to use data from every purchase to help identify further opportunities to influence customers towards healthier choices.
And new nudges are always popping up. In November 2019 a new DnaNudge shop opened in London. Combining a wristband and app, DnaNudge aims to help users make better food shopping choices based on their DNA and lifestyle. Food is scanned using the wristband, which will then flash red or green based on its suitability for the owner's biological profile. A product with high salt content will flash red for a user with high blood pressure, for instance. DnaNudge, which recently showcased at CES 2020, is collaborating with Waitrose to study the effects of this approach on pre-diabetic customers.
Keeping up with the PACE
Food labels themselves can be also used to encourage healthy eating, by translating calories into walking time to nudge people into healthier choices. This approach is often called Physical Activity Calorie Equivalent, or 'PACE' labelling, and has shown promise in reducing the number of calories and the amount of food consumed by the public[7]. Some results in the UK have been so promising that the Royal Society for Public Health has called for PACE labelling to be introduced. Despite further research needed to assess its real-world impact, this nudge is likely to receive more attention in the near future.
Nudging us towards a healthier future
It's a sad fact that non-communicable diseases (such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes) still account for around 70%[8] of global deaths. Furthermore, many of these deaths are due to factors that the victim may be able to influence, with tobacco use, alcohol abuse, diet, and inactivity all contributing to that number.
While grocery retailers might not have a direct responsibility for commanding their customers to eat better, they do have the opportunity to play a huge role. As behavioural science becomes better-known around the world and savvy customers expect retailers to make it easier for them to make healthier choices, expect a tipping point soon at which the nascent nudge becomes the new normal.
References
- Supermarket policies on less-healthy food at checkouts, PLoS Med (2018)
- Healthy snacks at the checkout counter, BMC Public Health (2012)
- Larger partitions lead to larger sales Journal of Business Research (2017)
- Shopper marketing nutrition interventions Prev Med Rep (2015)
- 'Food Dudes': Increasing Children's Fruit and Vegetable Consumption. Cases in Public Health Communication & Marketing (2009)
- Health on the Shelf report, Royal Society for Public Health (2019)
- https://www.lboro.ac.uk/media-centre/press-releases/2019/december/labelling-foods-amount-of-physical-activity-needed/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
Keep Reading...Show less
Are you looking to increase your contactable Customer base? How much money are you losing on incorrectly identified Customer communications? Throughout our 30 years of big data experience working with clients across industries around the globe, we have found that maintaining contact through relevant Customer engagement is a crucial component of putting the Customer First.
Essential to preserving contact data is ensuring that you have the most up-to-date information from your Customers; not an easy task. On average, people in the United States will move an average of 12 times in their lifetime. United States Postal Service data indicates 14% of the population change addresses annually. As email contact has grown, it's important to note that, on average, 30% of people change their email addresses each year. This is driven by ISP or job changes, or just to stop being spammed. As people move away from home phones to primarily mobile devices, phone numbers are stabilizing as consumers maintain the same numbers through physical moves.
Contact data maintenance also includes an effective and trackable process for removing Customers who "opt out", unsubscribe or otherwise request to not be contacted. Beyond Customer fallout for not honoring their request, regulations such as GDPR and CCPA can deliver fines as high as €20 million, or up to 4% of the annual worldwide turnover of the preceding financial year (whichever is greater), for any violations.
So, how are you collecting and managing sensitive, frequently changing Customer metadata? These three questions can help you perform a quick data health check for your business:
- How flexible are our Customer data platforms? Can multiple departments use the same Customer master data profile?
- What are the accuracy requirements for each of our communication channels?
- How unique is our Customer data asset and how valuable is it to our company?
Here are the most common data management options we encounter across industries:
1.Internal:
Maintaining Customer information manually through an internal data team can be time-consuming and costly. It may require Customers to update their information online or through a call center, with an internal data team to validate the changes, and your Customer engagement team to be made aware of the changes so they can update their downstream systems. If you are in contact with your Customers on a weekly basis, this process will need to be on-going and thorough to accurately capture the data changes.
2.Third party:
Many third-party CRM systems and databases exist, often removing the manual steps from this process and may even automatically update Customer address information via online sources. In many cases this information is based on publicly available data or the USPS' address tools. However, these updates can verge on being "creepy" to many Customers. Automated systems do remove many of the manual touch points for your teams, but the information is then strictly provided by the third-party databases and processes. Additionally, downstream systems often still require updates from these tools to maintain the most correct Customer information across your data landscape.
While there are some hybrid models of options, here are the main pros and cons we have identified for the primary methods:
| Internal Pros | Internal Cons |
|---|---|
| The fastest method if you own and manage your data ingestion platform | Managing a metadata repository tied to your website or mobile platform may require significant improvements in your front-end systems and teams |
| Your internal security can ensure that personal data standards and protections are maintained | A true "Customer master" repository will require significant resources, a robust data governance structure and regular audits for both security and data accuracy |
| The easiest method for maintaining your Customer opt-outs and communication preferences | If there is a data breach from your systems, your company is 100% liable for the breach |
| Platform and tool agnostic. An internal "Customer master" repository can serve as a single source of truth for Customer data within your organization | |
| Leverages the information provided from your Customers which in practice should be the most trusted |
| 3rd Party Pros | 3rd Party Cons |
|---|---|
| Removes significant pressure from your internal teams and systems as you are pushing the process to the 3rd party | May require you to maintain your own Customer opt-outs and communication preferences external to their platform |
| If the data resides on and is consumed from their systems, on-going security becomes less of a concern for your internal teams* | May not allow Customer provided information to be captured or maintained |
| Can be a very accurate source if they are leveraging governmental and legal databases | May require the use of their specific software and technology, limiting the ability for your organization to create an internal "Customer master" on your own databases and downstream systems |
| May be updated on a real-time basis from their systems | You are tied to the 3rd party data match and update process dependencies. Additionally, some companies limit the daily number of requests or queries |
| APIs and other data integration points with the 3rd party may be made available ensuring that all internal teams have the same "Customer master" | Are they consuming publicly available data (ex. mortgages and legal proceedings) or are they using some large unmanaged database to match Customer details and data? |
| How often are they confirming the accuracy of their data? Example "John Smith" may simply be a typo from years ago or it could be correct. How do they confirm accuracy? | |
| *If the 3rd party or their associated processors breach your Customer information, you may still suffer reputational and financial consequences |
Regardless of your chosen data mastering methodology, the Customer's preferred data should always be treated as the "most trusted," as this is the data your Customer is asking you to use. We recommend prioritizing Customer-provided data over other sources, only falling back on alternate sources if there are issues with Customer communications.
dunnhumby can help your company develop a comprehensive Customer mastering solution, regardless of your existing CRM process, technology or vendor. We have spent the last 30 years working with Customer data in many different stages of maturity and complexity. Through this process, we have developed proven best practices to collect and maintain your Customer metadata. If you are interested in discussing Customer mastering or Data Consulting, please reach out to your dunnhumby client representative or Contact Us.
Keep Reading...Show less
Grocery eCommerce: You won new online customers during COVID-19 – now how will you keep them?
October 26 2020
It's a well-worn phrase by now, but it's true that the COVID-19 crisis has drastically altered the global retail landscape. Here in the Asia-Pacific region, a majority of markets are now looking past the panic of the first wave and towards the future. In this series of articles, we'll explore how grocery retailers must adapt to a more omnichannel reality to thrive in a post-pandemic world.
The new wave of online grocery customers
Throughout the COVID-19 crisis we've seen the sharp rise and fall of many trends. As countries veered from one phase of the pandemic to the next, we've seen everything from panic-buying and stockpiling, to a booming demand for hygiene products. While some of these trends have stuck, the resumption of a more 'normal' life in many parts of the Asia-Pacific have seen others tail off.
One trend which is set to stay is in eCommerce, particularly within grocery. Lockdown drove a surge to online grocers the likes of which we have never seen – and it seems customers have been convinced by the online experience. According to multiple recent studies[1] China's grocery eCommerce market, already a booming sector with 29% growth last year, is now tipped to grow by 60% this year as the coronavirus has driven whole new segments of customers to the online grocery market. The trend is also sustaining; the main growth driver in JD.com's record-breaking '618' event this year was grocery, with sales almost doubling[2].
While general retail has been building momentum online for some years, grocery has been something of a laggard, rarely accounting for more than 15% of the overall grocery market. Historically the major barrier to entry to online grocery has been trust – over 50% of customers do not trust online grocery deliveries to pick the freshest and best items[3]. For years this has been a catch-22 scenario for retailers: customers don't trust the quality of online grocery because they haven't tried it, but they won't try online grocery because they don't trust the quality.
COVID-19 has caused a new wave of customers to finally take a leap of faith into digital grocery. Retailers can be happy that they've won new customers online, but now comes the hard work of retaining them.
The need for Customer Infrastructure
Much has been made of retailers' attempts to keep up with surging online demand during the early phases of the pandemic. Even in globally advanced eCommerce markets like the UK, the lead retailer has had to significantly expand delivery capacity to keep up with demand[4]. In order to meet the needs of new customers, retailers have rightly focused on having the right physical infrastructure in place.
However, if retailers want to keep meeting the needs of customers, they'll now need to focus on a different kind of infrastructure - the online customer experience.
The ease of shopping online is a double-edged sword for retailers. If customers can shop online with one retailer, they can shop online with any retailer. Your competitor store is no longer 1 kilometre away, it is one click away. Customers can literally browse competitor shop windows while they are in your store, and for countless retailers in the Asia-Pac region where online sales have historically been low, their digital stores may be looking rather outdated.
So while you may have won new customers, the fight to keep them is much more challenging.
Getting the digital experience right
The principles of great customer experience online are the same as instore. It's about helping customers easily find what they want. It's about helping customers feel they've got a good deal. It's about having a well-laid out store. Fundamentally, a great digital experience is about putting customers first and responding to their needs. Thankfully, the nature of eCommerce makes it possible to know these needs in detail through the wealth of data available to retailers. The data you're likely already collecting will tell you everything required to build a better overall and individual shopping experience for each customer who shops online.
Here are 3 ways retailers can act now to build a winning customer experience online:
- Bring the offline online
Your customers may be new online, but many of them will be existing offline shoppers. Their loyalty card history enables you to show them items they already buy. Better still, predictive data science can detect which of those items are staple and regular purchases that each customer might need right now – helping them quickly and efficiently build a basket based on their own personal behaviour. This knowledge can also help act as an online virtual assistant, helping customers find substitutes for out of stock products and prompting them with items they may have forgotten to add at the checkout. - Make it easy to find value
In a world where customers can price compare at the flick of a tab, maintaining price perception is vital. This is easier said than done online, as customers won't spend time browsing the 500 products you have on special that week. Instead, use relevancy algorithms to curate your promotions list at the customer level using their previous behaviour, and show each customer the offers that actually matter to them. - Optimise the navigation
Newer online customers tend to use online search and taxonomy functions much more than experienced online shoppers. If your online category flow is unclear, difficult to interpret or poorly arranged, shoppers will have a harder and more frustrating experience. Equally, if their searches lead to incorrect or blank results, customers will quickly lose patience. Site analytics data in the hands of an expert is a goldmine for optimising the online navigation – from naming and arranging categories in a strong taxonomy to eliminating poor-performing searches.
Retailers in Asia have a limited window of time to win the continued business of new online customers. As these customers become more familiar with the experience, the greater will be their demands and their likelihood to look elsewhere when their experience is sub-optimal.
At dunnhumby, we've been advising grocery retailers on digital best practise for over 10 years, led by 30+ years of leading experience in data science and we have developed a range of products for retailers to deliver exactly these kinds of industry-leading customer experience online, powered by retail data.
In the next part of our series on the post-COVID landscape in Asia-Pacific, we'll explore the diverging needs of customers in the wake of the pandemic, and how omnichannel personalisation can help retailers meet those needs efficiently and effectively.
[1] E-commerce drives China's stay-at-home economy in coronavirus aftermath & China's online grocery sector set for explosive growth, says GlobalData
[2] Chinese shoppers are staying online. That's great news for JD.com
[3] Study cites barriers to online grocery shopping
[4] Tesco Delivers One Million Online Orders In A Week In The UK
Keep Reading...Show less
labeled box lot
Photo by Franki Chamaki on Unsplash
Article originally appeared on Forbes.
My company recently produced a report on the state of the food retail industry, and in studying that sector, we discovered something that we hope will make food retailers stand up and listen. We learned that the nation's top grocery chains have found a way to focus on both short-term financial performance and investment in long-term consumer engagement. The latter is considered an insurance policy for the future — a sobering thought in the new year.
Insurance for the future may be one of the most difficult things to buy if you are overly concerned about present-day financial performance. As a consultant and provider of technology services to food retailers all over the world, I understand why they are concerned. Despite positive projections for the industry in 2019, there are signs that the economy is slowing, and that could very well soften consumer spending.
There's also the continuing threat from digital disruptors like Amazon that might coerce retailers into taking actions, such as blindly lowering prices, that further erode margins that are already razor thin. Another threat, well known to the industry but perhaps less so to the general public, is the new generation of discount chains that have figured out the magic of balancing short and long-term strategy and planning.
But here's the biggest challenge facing food retailers: falling prey to fear itself. I'll admit that fear can sometimes be a helpful motivator to monitor and manage your business. A recent article reported the one photo that the CEO of Walmart keeps on his phone. It lists the top 10 retailers per decade over more than sixty years, and it serves as a reminder for how many companies come and go. But McMillon is managing fear, not falling prey to it. Retailers can manage their fear, rather than fall prey to it, by leaning on three tools that can alter their standing in the industry.
Data
Recent years have brought with them the dawning realization that retailers possess abundant consumer data. Gathered and culled from direct interactions between stores and their customers, data of this quality helps retailers price and promote their products more intelligently. It helps them with product assortment, store design and managing the new kinds of services they offer. This can include things like in-store pickup and options for self-service, depending on what makes sense for their customers. More profoundly, data can help retailers think about how they can monetize that data to help their vendors connect more meaningfully with customers. The reality is that all grocery retailers potentially are media companies, with access to online and offline media properties. It's a lesson learned from Amazon, but a small number of retailers around the world are helping to raise their profit margins by taking a page from the playbook. The place to start is with first-party customer data, which is what retailers uniquely possess.
Relationships
For food retailers especially, we learned that there is an enormous number of inefficiencies with how food retailers engage with vendors, beginning with how they collaborate on pricing and promotions. Some retailers are struggling to move beyond spreadsheets to other systems that help automate exceedingly detailed work. We are living in a time where inefficiencies can make or break a business. But still, many food retailers are ready to concede that times have changed. Beyond providing technology that moves beyond spreadsheets, retailers would benefit from interviewing their vendors to discover what would make life easier for them in this highly competitive industry.
Strategy
Change may be painful, but inertia will be lethal.
As the celebrated business scholar Clay Christensen has written, it is very difficult for any business to change course on a strategy that had made it successful in the past. He calls this the innovator's dilemma because, at almost any time in the evolution of any industry, leaders must understand that a decision regarding the future must be made.
To that end, the future is not served by signing a partnership with a third-party fulfillment provider to launch an e-commerce service. It's about making better decisions that impact the core of your business and operating more efficiently to better serve your customers across all of your channels.
But here's where food retailers have a unique opportunity, at the beginning of 2019, to ignore fear and take a small leap into becoming more viable by making decisions based on what they know about their customers. There is no business that knows more about people than retail, because they actually meet and greet them every day.
Take heart, and fear not. This is only the beginning of a story that's mostly yet untold.
Keep Reading...Show less
Customer First Radio Episode 5 | Ted Eichten, Head of Price & Promotions, North America for dunnhumby
April 21 2021
FOR RETAILERS
Smarter operations and sustainable growth, powered by Customer Data Science.
FOR BRANDS
Better understand and activate your Shoppers to grow sales.
Customer First Radio Episode 4 | Daryl Wehmeyer, Head of Category Management, North America for dunnhumby
February 17 2021
Retail leaders must objectively understand how their business currently considers Customers before trying to set a more Customer-centric direction and focus. There are some formal assessment methodologies, like dunnhumby's Retail Preference Index (RPI) and Customer Centricity Assessment (CCA), which offer detailed evaluations of a business' capabilities, strengths and weaknesses based on Customer perceptions (RPI) or global best practices (CCA).
The approach outlined below is not intended to replace these formal tools; rather, these observations are intended as a kind of 'toe in the water' to help retail leaders form early hypotheses and points of views. These are rules of thumb, heuristics culled from global experience. Later, leaders might use these observations to informally check progress from time to time as a way of assessing whether the "program in the stores matches the program in our heads".
Hence, the context and laboratory for these suggestions is the retail store, where the rubber meets the road, so to speak.
1. Who really runs the store?
Walking around a store (or better, walking around several), can give many clues toward understanding a retailer's attitude about its Customers, as well as revealing some of the challenges ahead for installing Customer First. As Customers ourselves, we are qualified to assess an organization's 'readiness' for Customer First, simply starting by walking around.
How a Customer experiences the store shapes their perception of the brand, and there are dozens (even hundreds) of 'moments of truth' for Customers in each shopping trip – opportunities for the retailer to win more loyalty, or indeed to lose it. And it only takes one 'bad' experience to erase all the good.
Leaders can form an opinion about the Customers' true shopping experience by observing 'Who really runs the store?' – a way to put on a Customer lens to assess if the Customer, the retailer, the supplier, or no one is driving shopping experience decisions, like range and presentation. For example:
- Choose three sections across the store (telling categories include yogurt, pasta sauces, milk, and packaged lunch meats). Look to see how the product is organized and presented (remember to try to see through the eyes of a Customer).
- Is the section organized by brand (e.g. all Danone yogurt is merchandised together in a recognizable Danone brand block)?
- By Customer benefit or usage (e.g. all brands of probiotic yogurt are merchandised together, as are all Greek style yogurts, all kid's yogurts, etc)?
- Or, by some hybrid but logical planogram rather random plan, with little recognizable logic at all?
- Would you conclude that the product display / layout logic is influenced more by supply chain, by brands, or by the Customer need states or trip missions?
- How broad is the range (e.g., number of varieties or sizes)? How deep (e.g., number of brands of the same flavor or variety)? Does the breadth and depth feel Customer friendly, or confusing?
Of course, analysing any available loyalty data will later tell us how Customers shop the category and that might well be by brand (or flavour or size, etc., and will certainly vary by section). But this first assessment helps us begin to form our perspective on how tuned-in the business is around its Customers, and about where within the business leaders might need to begin to install insights and the Customer language.
2. What messages are Customers receiving?

Store signage not only delivers a written message, but also a type of 'body language' that Customers tune in to, albeit not always consciously. Look around the store to see both the written and hidden messages, and hear the tone being communicated: ask, do messages speak respectfully to Customers? For example:
- Signage at the entrance rudely telling Customers what the rules are, even though 99.999% of Customers will never even think of shopping without shirts or shoes, or wearing roller blades
- Narrow limits on the quantities of promoted products or services.
- Rules and restrictions, terms and conditions.
- Aggressive security barriers and gates at entrances – although sometimes operationally necessary, these also tell honest Customers that they, the shoppers, are not to be trusted.
- Phony expiration dates for promoted prices – Customers learn that the deal will be repeated soon, if not immediately. Best example is the many carbonated soft drink promotions below shelf price that are repeated frequently, and the innumerable 'roller' prices practiced by many retailers.
- Stupid pricing signs (any stupid sign, really).
3. What messages are Employees receiving?

While walking the store, traveling through stock rooms and the employee break room, note the signage and messaging aimed at staff. What seems to be valued more – numbers or people?
What policies and rules guide employee behaviour?
How are they expected to interact with Customers?
Are the messages respectful of staff? Of Customers?
What do signs say about the culture around Customers?
4. Who has the power to satisfy Customers?
dunnhumby's Loyalty Drivers analysis suggests that Customers exhibit four 'mindsets' in their shopping journey – Discover, Shop, Buy, and Reflect. One element of the 'Reflect' mind-set includes the decision to return, exchange, or to request a refund when the product or service does not quite suit.
On your store walk, observe who has the power to satisfy Customers making a return or wanting a refund: is the front-line employee empowered to satisfy the Customer, or must the Manager be called? Is there one 'service' desk where Customers must queue to get their money back, or can the helpful cashier make it good on the spot?
Examine the return policy to assess its sensibility and ease from a Customer viewpoint. For example, must a Customer act within 7 or 30 days, and is a receipt required and signature under penalty of perjury? Is the taking of an oath necessary, or perhaps a drop of blood? The store's practice says volumes about who deserves trust in the eyes of the business. Requiring levels of approvals and higher management involvement (or some other form of hoop-jumping) is neither trusting of employees nor Customers.
The return / refund policies and practices are strong indicators of a company's readiness for, or progress along the Customer-centric journey. Customer First organizations give front-line employees broader authority to resolve Customer needs, and extend the power to satisfy Customers to most members of staff, in some form. For best practices in this area, please see the policies from Nordstrom in the U.S. and Ritz-Carlton globally.
5. Do the words of your leaders matter?
Senior leaders set the tone for how Customers are regarded and treated in the business both by their words and their actions, of course. And the C.E.O.S – Customers, Employees, Owners, and Suppliers – all take notice. It's widely documented that leaders who walk the walk are more effective than those who only talk the talk.
One simple yet powerful way to assess readiness and progress is seeing how leadership's walk and talk align. A word cloud, like the one illustrated below, makes the point very clear. In this example, recent shareholder statements (same quarter) were compared for two companies on a Customer-centric journey. We can see different progress in a form of 'walking the walk' at Retailer X and Retailer Y. The C.E.O.S are hearing what really matters to the leaders, and are forming the Customer culture accordingly, all the way down to store level.

Implications for retail leaders
The store shapes Customers' perception of the brand; there are hundreds of opportunities for the retailer to win or lose loyalty in each shopping trip. Customers take clues, consciously and unconsciously, throughout their entire shopping experience, and draw conclusions about retailer warmth and attitude toward shoppers. And it only takes one disappointing experience to erase all the good.
Retail leaders must take an objective assessment of the shopping experience using a Customer lens to understand their current state and readiness for customer centricity. Pay close attention to the body language and tone of your policies. Store signage, employee empowerment and communications, and practices around assortment and presentation are clear indicators of the organization's attitude about the Customer.
Who actually runs your store?
This is the first in a series of LinkedIn articles from David Ciancio, advocating the voice of the customer in the highly competitive food-retail industry.
Keep Reading...Show less
Photo by Jonathan Velasquez on Unsplash
In the first episode of Customer First Radio, Dave Clements, Global Head of Retail for dunnhumbyand David Ciancio, Global Head of Grocery for dunnhumby kick off the series by discussing what it means to be a truly Customer First business, share which retailers and brands today embody a Customer First mindset, and examine how Customer First materialized during the pandemic with retailers.